Small Language Models (SLMs) are AI systems trained on billions of parameters (not trillions) that achieve 70–90% of GPT-4’s performance at 1/50th the cost. They run on consumer hardware, offer privacy control, and are increasingly dominating enterprise AI deployments.
Small Language Models:I made a mistake in 2024. I thought AI had to be big to be smart. I was wrong.
For three years, I watched the industry obsess over bigger models. Bigger meant better. More parameters meant more capability. We saw it with GPT-3 to GPT-4, and everyone assumed that was the only direction forward.
But late 2025, something shifted. The smartest teams stopped asking “how big can we go?” and started asking “how small can we go without losing performance?”
That shift is creating one of the biggest opportunities in AI right now. And if you’re building anything with language models, you need to understand why.What Are Small Language Models (SLMs)?
Small Language Models are AI systems trained on significantly fewer parameters than Large Language Models. While GPT-4 has around 1.8 trillion parameters, SLMs like Microsoft’s Phi or Google’s Gemini 2B operate with just billions of parameters.
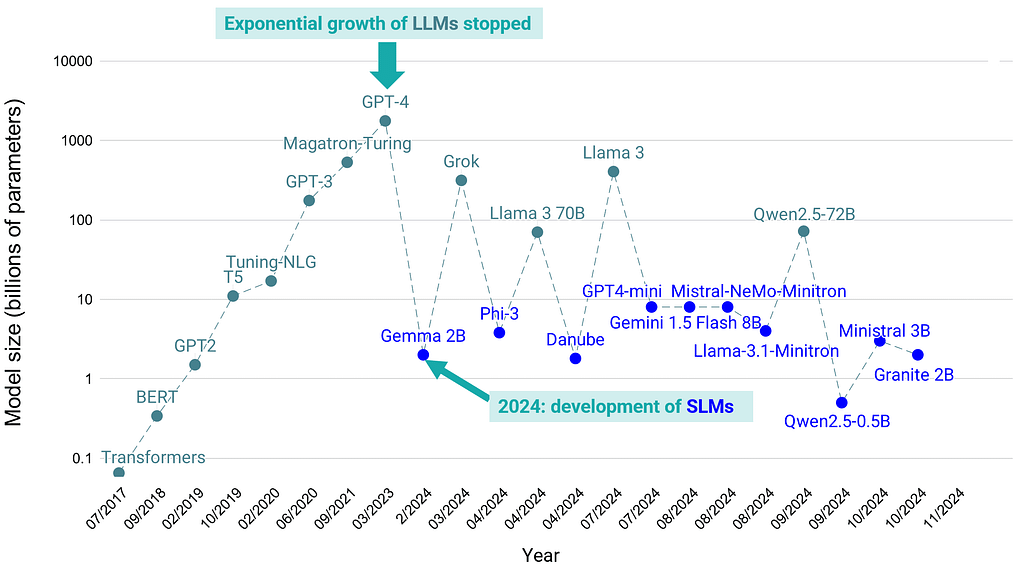
The critical insight: fewer parameters don’t mean less capability anymore. Modern SLMs are achieving 70-90% of the performance of larger models on specific tasks, while being 10-100x smaller and infinitely more cost-efficient.
Think of it like this: you don’t need a massive truck to move furniture within your apartment. A small, efficient vehicle works perfectly for the job at hand.
Why Small Language Models Are Beating Large Language Models for Enterprise
1. Cost Efficiency
This is the biggest win. Running a 7B parameter model costs $0.01 per 1M tokens. Running GPT-4 costs $0.03 per 1K tokens. The difference? Orders of magnitude.
For enterprise applications processing millions of requests daily, SLMs reduce infrastructure costs by 85-95%.
Real example: one enterprise using Phi 3.8B for customer support handled 1M queries per month for $500 total. The same workload on GPT-4 would cost $30,000/month. Annual savings: $354,000. Development cost to fine-tune on internal FAQs: $5,000. ROI payback: 17 days.
2. Speed and Latency
Smaller models mean faster inference. SLMs can run on consumer GPUs, edge devices, or even CPUs. Response times drop from 2-3 seconds to milliseconds.
For real-time applications like customer support, recommendation engines, or autonomous systems, speed is everything.
3. Privacy and Control
SLMs can run on-premise or on your own infrastructure. No data leaves your servers. No vendor lock-in. No worrying about data being used to train someone else’s model.
Enterprise compliance teams are celebrating this.
4. Customization
Small models are easier to fine-tune. Want a model specifically trained on your industry jargon, customer data, or internal processes? SLMs make this practical and affordable.
Large models? You’re paying thousands to dozens of thousands just to customize them.
The Real Opportunity: Specialized SLMs
The smartest companies aren’t trying to build “generalist” SLMs. They’re building specialized models for specific tasks:
- Customer support SLMs trained only on FAQ and chat data
- Code generation SLMs trained only on programming languages
- Medical diagnosis SLMs trained only on medical literature
- Legal document SLMs trained only on contracts and regulations
A specialized 3B parameter model beats a generalist 13B parameter model on its specific task. Every single time.
Examples Proving the Shift
Apple’s Private Cloud Compute: Uses on-device and edge processing with small models instead of sending everything to servers.
OpenAI’s GPT-4o mini: A “small” version of GPT-4 that’s 90% cheaper and 60% faster for many use cases.
Meta’s Llama 3.2: Explicitly optimized for edge devices with 1B and 3B versions that outperform much larger competitors.
Microsoft’s Phi series: Achieves competitive performance at 3.8B and 14B parameters through better training data and techniques.
SLMs vs LLMs: Quick Comparison
| Metric | SLMs (Phi, Llama) | LLMs (GPT-4, Claude) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost per 1M tokens | $0.01 | $0.03–$0.30 |
| Inference latency | 50–200ms | 2–5 seconds |
| Fine-tuning cost | $100–$500 | $1,000–$10,000 |
| Privacy (on-premise) | ✅ Yes | ❌ No |
| Reasoning quality | 7/10 | 9/10 |
How to Leverage SLMs Today
If you’re building anything with language models, here’s your action plan:
1. Identify Your Actual Use Case: Do you really need GPT-4? Or would a specialized model handle 95% of your use cases?
2. Start Experimenting: Open-source SLMs like Llama 3.2, Mistral, and Phi are available on Hugging Face. Test them.
3. Calculate Your ROI: Compare inference costs. A $10,000 annual savings on processing might dwarf your development time.
4. Plan for Customization: SLMs are small enough that fine-tuning on your specific data becomes cost-effective.
5. Think About Privacy: If you’re handling sensitive data, on-premise SLMs eliminate entire classes of compliance headaches.
The Bottom Line
I was wrong in 2024. Bigger isn’t always better. The smartest approach isn’t choosing between large and small models—it’s choosing the right model for the right problem.
SLMs are becoming the standard for enterprise AI. They’re cheaper, faster, more private, and easier to customize. If you’re not exploring them yet, you’re leaving money on the table.
The future of AI isn’t about building bigger models. It’s about building smarter ones.
Q: Will Small Language Models replace Large Language Models entirely?
A: No. Large Language Models will remain useful for research, novel problem-solving, and tasks requiring broad knowledge. But for 80% of enterprise use cases, Small Language Models are now the better choice.
Q: How do I fine-tune an SLM on my data?
A: Libraries like Hugging Face’s transformers make it straightforward. You’ll need GPU resources and training data. Cost ranges from $100 to $5,000 depending on model size and dataset.
Q: Are open-source SLMs production-ready?
A: Yes. Llama 3.2, Mistral, and Phi are all production-grade. Use them with confidence.Q: What is the difference between Quantization and Distillation?
A: Quantization shrinks a model by reducing its precision (bits), while Distillation involves training a smaller ‘student’ model to mimic the behavior of a larger ‘teacher’ model.
Q: Will SLMs replace LLMs?
A: No. They will coexist. LLMs will be used for heavy reasoning tasks, while SLMs will handle fast, repetitive, and privacy-sensitive tasks.
Author Bio: Sudhir Dubey is an AI researcher and data science educator focused on practical AI deployment and fine-tuning strategies for enterprise use cases.



